
You will need evaluation methods most common in eCommerce accounting to achieve your goal. In this post, you will understand what the account inventory cost method is and what it involves. In the end, you will know how to calculate the average cost, how your business can benefit from it, and its application. Average cost method, or weighted average, is one of the inventory valuation methods that help to calculate the cost of goods sold. In terms of cash flow, the average cost method can influence how businesses manage liquidity.
Understanding the Average Costing Method
It would be best if you had consistency when managing your inventory levels so that the process of filing taxes and comparing financial years becomes easier. Depending on what you are selling, the Average Cost Inventory method is the best option compared with the other methods. You can maintain your financial statements’ accuracy and track the value of inventory every year for proper accounting while you save time doing it. In conclusion, the Average Cost Method provides a practical and versatile approach to inventory valuation. Its simplicity and ability to smooth out cost variations make it a valuable tool for businesses seeking a balanced and straightforward method for tracking and valuing their inventory. It’s important to note that the Average Cost Method can be applied in both periodic and perpetual inventory systems, offering flexibility for different accounting practices.
A Summarized Guide to Inventory Costing Methodologies
It assigns value to the cost of goods sold (COGS) by using the weighted average of all the inventory that the company purchased during a period of time. The period could be a month, quarter, or annual period, so long as it remains consistent. In addition to assigning value to the cost of goods sold, it also assigns value to the cost of goods that are still available as inventory. Standard costing is when companies assign the expected (or standard) costs of material, labor and overhead to inventory, rather than the actual costs. This management tool helps to plan budgets, manage and control costs and determine how successfully a company controls cost. The Pacific Bead Company sells handcrafted beads from local island crafters to retail markets and customers out of its warehouse.
What Inventory Cost Methods Are Acceptable Under Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP)?
A consistent valuation of inventory can lead to more predictable cash flow patterns, as the cost of goods sold is not skewed by the timing of inventory purchases. This predictability can aid in budgeting and ensure that cash reserves are maintained at levels sufficient to meet operational needs. From a financial analysis perspective, the average cost method can influence key ratios such as the current ratio and inventory turnover ratio.
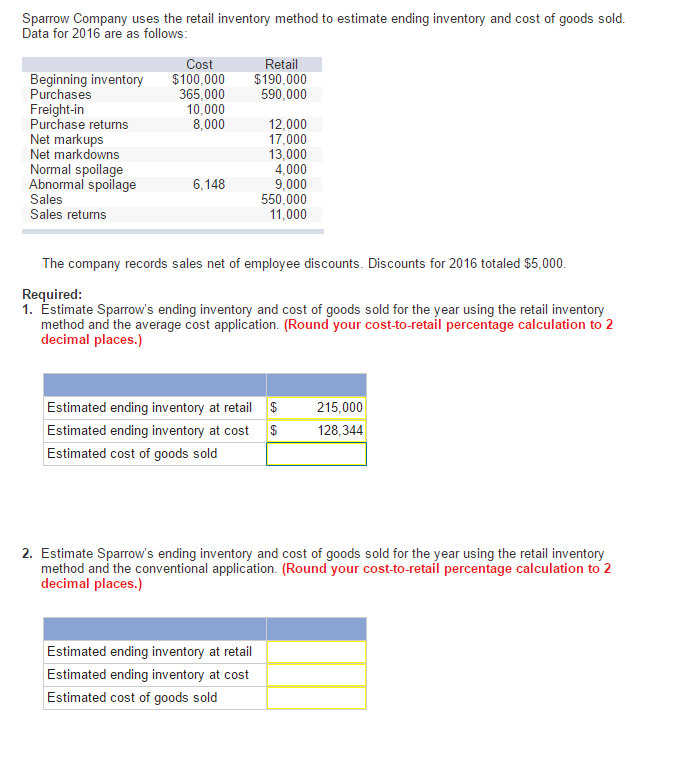
It calculates the cost of ending an inventory against the cost of the goods sold in a particular period based on the weighted average cost per unit of inventory. The average cost method is one of the three methods of inventory evaluations, with the other two being the First in First (FIFO) and the Last in First (LIFO). Once your business chooses an inventory valuation method, it must use it consistently to comply with the generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP).
- Ensure that the method of inventory costing that you choose remains the same throughout.
- The consistency principle requires a company to adopt an accounting method and follow it consistently from one accounting period to another.
- Standard costing is when companies assign the expected (or standard) costs of material, labor and overhead to inventory, rather than the actual costs.
There are different ending inventory and COGS for perpetual versus only yearly periodic systems. If companies apply LIFO in a perpetual system, they need to use special adjustments to take advantage of using the LIFO method for tax accounting. However, a manufacturer would report inventory at the cost to produce the item, including the costs of raw materials, labor and overhead. By averaging the costs of all inventory items, ACM simplifies the calculations related to the cost of goods sold (COGS).
Besides FIFO and LIFO, the Average Cost Method is another returning to school after heart or heart common way for accountants to value inventory.
Average cost method is a simple inventory valuation method, especially for businesses with large volumes of similar inventory items. ACM works by taking the total cost of goods purchased or produced during a period and dividing it by the total number of items purchased or produced. This gives an average cost per unit, which is then applied to both the cost of goods sold and the ending inventory. This approach ensures that inventory valuation remains consistent, regardless of fluctuations in purchase prices throughout the period. It takes cost of goods available for sale and divides it by the number of units available for sale (number of goods from beginning inventory + purchases/production). A physical count is then performed on the ending inventory to determine the number of goods left.
A fluctuation in the cost of a stocked item can lead to errors in reported sales profit. As such, your pricing may never recover the cost of more expensive items, which means losses. With the advantages of Average Inventory costing aside, let’s look at a few drawbacks of the method. Let’s have another tabulated example and apply the formula to understand the Weighted Average Cost. At the end of the year, the last Cost per Unit on Goods, along with a physical count, is used to determine ending inventory cost.